Is it a requirement to maintain documented information on legal and other requirements.
Why?
Risks and opportunities to your organization may arise from them. These may be positive or negative and should be investigated and monitored using a 'Requirements Register'.
Contents
- 6.1.3 Determination of Legal and Other Requirements
- Examples
- Step 1: Identify Relevant Health and Safety Legislation
- Step 2: Evaluate Legal Requirements Arising from Legislation
- Step 3: Document Legal Requirements
- Step 4: Determine Applicability of Other Requirements
- Step 5: Review the Legal Requirements Register
- Step 6: Monitor Compliance
- Legal & Other Requirements Procedure [Template download]
Applicable laws and regulations or voluntary commitments — such as organizational and industry standards, contractual relationships, principles of good governance and community and ethical standards.
Our Legal & Other Requirements Procedure is proven to work.

Maintain an indexed list of relevant legal requirements, and other requirements such as standards and procedures in connection with identified safety critical tasks and associated hazards by referencing the minimum acceptable legal, industry standards and technical specifications against the associated equipment and operating routines.
Ensure that all identified occupational health and safety hazards are evaluated and understood in terms of current legislation, including as appropriate:
Legal and other requirements which are relevant to your organisation can be identified using websites such as:

The Health & Safety Manager should assess all relevant occupational health and safety related legal requirements, regulations and Approved Codes of Practice (ACoPs) using http://www.legislation.gov.uk that are applicable to your operations, have been identified and evaluated to assess their potential impact on the company’s operations.
The company should evaluate its compliance with legal requirements on an annual basis. This will involve a review of current and any new legislation. An evaluation of legal compliance will be undertaken from the Legal Requirements Register. (Codes of Practice and HSE & Environmental Agency guidance will also be considered).
Where regulations, permits and consents contain specific compliance requirements, these should be incorporated into your objectives and your mechanism for setting targets. Other requirements will be identified through interested parties, such as insurance brokers and insurers’ requirements, and those imposed by the Institute of Occupational Safety & Health (IOSH) or the requirements of Membership to ROSPA, IOSH, CRONER, etc.
Our Legal & Other Requirements Procedure is proven to work.
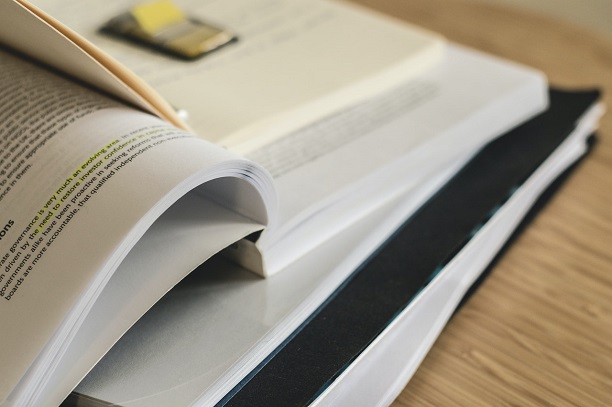
The evaluation of legal requirements should be documented within a Legal Requirements Register in order to identify and demonstrate applicability of how the company complies with current health and safety legislation.
Following the initial assessment of the legal requirements, consider capturing the relevant information into a document. A spreadsheet may be useful for this purpose. The Legal Requirements Register includes a brief description of the requirements of each regulation and how your company complies with legal requirements.
Other requirements will also be identified and be considered through interested parties. Any requirements will be entered on the Legal Requirements Register. Additionally, the Legal Requirements Register should be saved on the company network to ensure staff access.
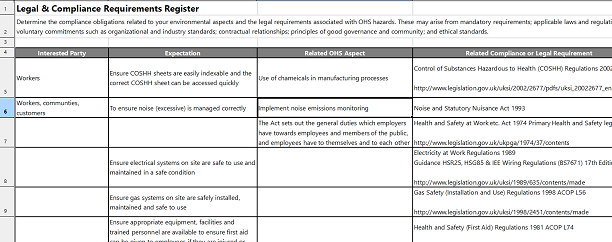
Legislation |
Description |
Requirements |
Evidence of Compliance |
Actions |
Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (SI 2677), as amended 2004 (SI 3386), |
The COSHH Regulations require employees to carry out an assessment of health risks created by substances hazardous to health. |
Must ensure that risk assessments are undertaken and controls implemented for any process where it is likely that workers may be exposed to a hazardous substance covered by these regulations. This includes storage of the substances. |
COSHH sheets, risk assessments etc. are available at point of use/ potential incident. Training given to affected employees |
Hazard identification and risk assessment procedure, COSHH assessments |
Ensure COSHH sheets for relevant materials are in the workshop |
||||
Ensure COSHH sheets are easily indexable and the correct COSHH sheet can be accessed quickly |
||||
Ensure ALL new, or one-off products have a respective data sheet. |
||||
Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 |
The Act sets out the general duties which employers have towards employees and members of the public, and employees have to themselves and to each other. |
Provision and maintenance of plant and systems of work that are safe and without risks to health |
Auditing and monitoring |
Health and Safety Policy and all supporting system documentation and processes |
Ensuring safety and absence of risks to health in connection with the use, handling, storage and transport of articles and substances |
PPE issue records Material Safety Data Sheets |
Health and Safety Policy, training, hazard identification and risk assessment procedure, Risk COSHH assessments, Inspections, Storage and Usage sheets & Training |
||
Provision of information, instruction, training and supervision as is necessary to ensure the health and safety at work of employees |
Training records, staff briefing records |
Training and consultations, Fire risk assessments, training records and emergency plans, safety signage |
||
Maintenance of facilities must be in a condition that is safe and without risks to health and the provision and maintenance of means of access to and egress from it that are safe and without such risks |
Insurance certificate on each noticeboard |
Risk assessments, inspections, maintenance schedules and pre-use checks, permits to work, emergency and evacuation plans |
||
The provision and maintenance of a working environment for employees that is safe, without risks to health, and adequate as regards to facilities and arrangements for welfare |
Service records & schedules |
Gas safety engineers, service reports and Gas Safe register. Compliance certification and PAT testing registers, Fire risk assessments, inspections |
Other requirements include the requirements of interested parties and workers, national and international standards, contract requirements, business codes, guidance notes, code of practices, other technical memoranda and other practice notes produced by government agencies as well as professional institutions.
Other requirements can result in risks and opportunities to your organization. The needs and expectations from interested parties only become requirements for an organization if it chooses to adopt them.
Our Legal & Other Requirements Procedure is proven to work.
The Legal Requirements Register (included in our OH&S Template) should be reviewed for adequacy (both for new regulations and updated regulations) at least once a year by the Health and Safety Manager who will report findings during the Management Review meetings. HSE updates occur during April and October each year.
The Health & Safety Manager evaluates compliance with legal and other requirements on an ongoing basis and through various means, and via http://www.legislation.gov.uk, which assists your organization in complying with its legal and other requirements.
Any changes to our legislative requirements must be communicated to the workforce and any other person who may be affected, e.g., contractors and where required, additional training should be provided for anyone affected by the changes.

Monitoring compliance with legal requirements and regulations is necessary to ensure that safety risk controls, applied in the form of regulations, are effectively implemented and monitored by your organization. The causes and contributing factors of any non-compliance should also be analysed and addressed.
The legal compliance audits are conducted by competent, in-house personnel or a qualified, independent third party. Competent personnel/third parties should hold a minimum of 2 years on-the-job-training or an equivalent combination of training and formal education in health and safety law and legal compliance.
The compliance audit frequency should be reduced when repeat compliance audits find zero non-compliances. The auditor should report legal compliance audit findings at the next Management Review meeting. Where additional legal requirements are identified when the list of legal requirements is reviewed by the compliance auditor, these must be reviewed and considered by Top management.
Ensure that the requirements of any new legislation may place on your organization are communicated to all relevant levels and functions within the business and are assessed through the internal audit process.
Updated: 12th April 2022
Author: Richard Keen

Richard is our Compliance Director, responsible for content & product development.
But most importantly he is ISO's biggest fanboy and a true evangelist of the standards.
Learn more about Richard

Don’t Try to Manage It All Alone!
Our ISO Auditors and Quality Manager Trainers have been in this industry for years, and since 2002 we’ve been providing thousands of small businesses and large corporations with the tools they need to get certified.
Instead of trying to create everything you need to follow this process from scratch, use ours. We have procedures, templates, checklists, process maps, forms and gap analysis tools to help you control your documented information without missing a single input or output.
Before you invest all the hours reinventing the wheel, before you spend countless dollars outsourcing the task — try our templates.
| QMS ISO 9001 |
EMS ISO 14001 |
OH&S ISO 45001 |
|
|
Legal & Other Requirements Procedure The purpose of this procedure is to outline your organization’s methodology for the identification of relevant legal and other requirements and ensuring the inclusion of the resulting safety requirements into our health and safety management system. The evaluation and review of relevant legal requirements is achieved through the provision of access to legal requirement databases and resources.
Forms & Reports also included:
>> Free Download - Control of Calibrated Equipment Procedure - this will give you a good idea of what to expect when you purchase the procedure. |
|
|
$19 USD |
Pay by Credit Card, Debit Card, PayPal or Apple Pay.

 |
Please read our Money Back Guarantee. |
Bought by Small Businesses and Large Corporations our templates have been sold online and CD since 2002.
Used by:
The Templates are used by first-timers following our step-by-step, clause-by-clause guidance documents; and experienced Quality Managers wishing to streamline and improve their existing documentation.
The application of our templates and OH&S manuals is scalable and generic; regardless of the size and type of organization. The elements that form the Health and Safety Management System Template are the same.
1. Our customizable templates save you time and money by offering a streamlined process to create your quality documentation
2. They’ve got everything you need in one simple template
3. Proven to work our templates have helped thousands of businesses big and small achieve certification
4. Documents use styles to make reformatting and rebranding a breeze
5. Our templates are generalizable for any industry or sector. The application of our templates is scalable and generic; regardless of the size and type of organization.